When we think of Minnesota, we often envision its frigid winters, with snow-covered landscapes and frozen lakes. However, this summer, Minneapolis reached an astonishing 97°F (36.1°C). While this may seem extreme, Phoenix, Arizona, has experienced a staggering 24 consecutive days of temperatures surpassing 110°F (43°C), leading to a surge in emergency room visits due to heat-related injuries.
What makes heat so harmful to us? How does our body react when temperatures rise beyond our comfortable range of about 70°F (21°C)?
Section 1.1: The Science of Body Temperature Regulation
The average human body temperature is often cited as 98.6°F (37°C), a figure established by German physician Carl Wunderlich in 1868. However, this is merely an average, with normal body temperatures fluctuating between 97°F and 99°F. Infants can even tolerate temperatures up to 100°F without serious issues.
In our core, where vital organs reside, we maintain a stable temperature. In our extremities, temperatures can drop to as low as 86°F (30°C) without adverse effects. When external temperatures exceed our internal temperature, our body initiates a sweating response.
“But wait!” one might say, “I start sweating when it’s only 85°F outside!” This occurs because the perceived temperature can vary greatly due to humidity levels.
The heat index, which reflects how hot it feels, is crucial. For instance, a 75°F room can feel like 69°F in 0% humidity but can feel like 80°F at 100% humidity.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Role of Humidity in Heat Perception
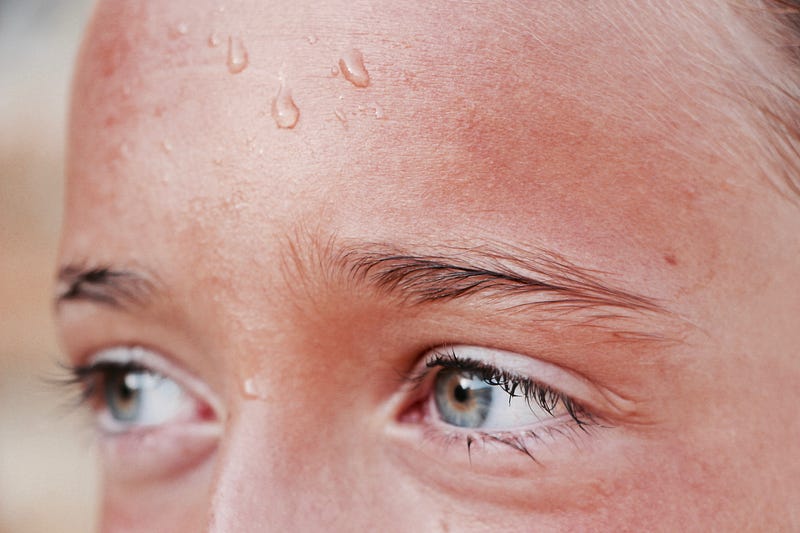
Section 1.2: The Body’s Panic Response to Overheating
As we endure excessive heat, our core temperature rises, prompting the hypothalamus to trigger sweating. The hotter it gets, the harder our body works to cool down. Our heart rate increases, aiming to circulate blood more rapidly to the skin, where heat can escape. This condition, known as hyperthermia, can be dangerous.
Each degree Fahrenheit increase raises the heart rate by approximately ten beats per minute, leading to symptoms like light-headedness and fatigue. Our immune system can react similarly to a fever, ramping up inflammation and pain as it searches for perceived threats.
The consequences of hyperthermia are severe and can affect nearly every organ in our body. Muscles may break down, releasing toxins into our bloodstream, while our gut lining becomes more permeable, increasing the risk of bacterial infections.
Our brain can also suffer, leading to hallucinations, seizures, or even coma. The heart may become overworked, potentially leading to heart attacks, while dehydration can halt sweating, exacerbating the rise in core temperature.
A core temperature nearing 106°F can cause protein denaturation, disrupting crucial biological functions. While there’s no exact temperature guaranteeing fatality, medical sources indicate that 101.4°F (38.5°C) presents a significant risk of death, with 104°F (40°C) being life-threatening.
