Unveiling the Deepest Living Fish Ever Documented: A New Record
Written on
Chapter 1: A Remarkable Discovery
A groundbreaking achievement has been made in marine biology with the discovery of the deepest living fish ever photographed, found at an astounding depth of 8,336 meters below sea level.
This significant finding comes from a collaborative scientific mission involving Japanese and Australian researchers, who focused their studies on the Izu-Ogasawara Trench. This trench is noted for being one of the Earth's deepest oceanic formations, with depths reaching up to 10 kilometers.
Section 1.1: Exploring the Izu-Ogasawara Trench
The team deployed an unmanned submersible equipped with a camera to explore depths just beyond 8,300 meters. At this extreme underwater environment, pressure levels soar to around 800 times that of the surface. Surprisingly, marine life persists even in these harsh conditions. A member of the Pseudoliparis genus, a type of demersal fish, was captured on film, demonstrating its ability to thrive in the hadal zone, which extends deeper than 6 kilometers.
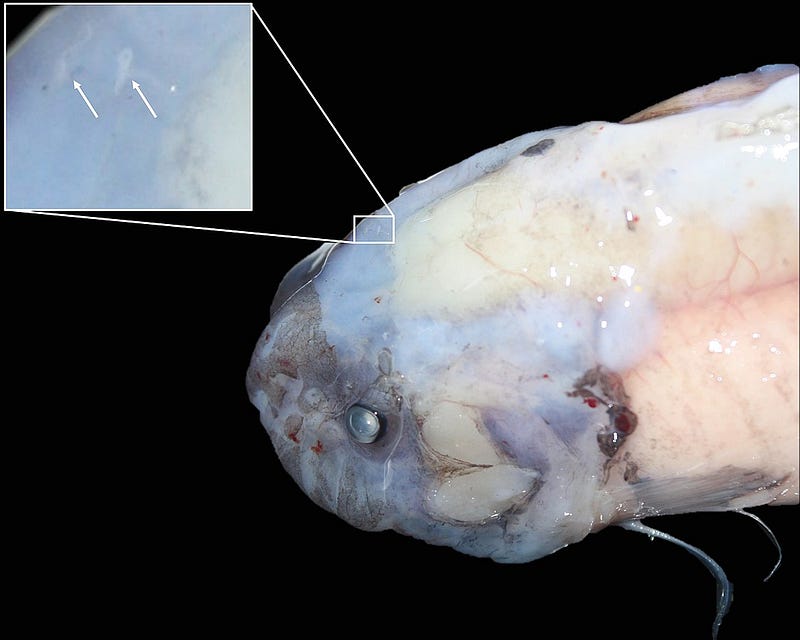
Subsection 1.1.1: The Appearance of the Deepest Fish
The recorded juvenile fish exhibited a striking blue hue that transitioned to silver, characterized by a long, flowing tail and a rounded head. Despite being filmed, this fish has yet to be classified, leaving its exact species unidentified.
- ..youtube:: TktdNurphxA
width: 800 height: 500
Section 1.2: Previous Records and Conditions at Depths
This remarkable fish now holds the title for the deepest living specimen ever documented, surpassing the previous record set in the Mariana Trench, where a fish was recorded at 8,178 meters in 2017. The scientific community long believed that deeper-dwelling fish could exist, but their habitats had yet to be explored thoroughly.
Chapter 2: The Unique Environment of the Deep Sea
Deep-sea fish adapt to a unique and stable environment marked by extreme darkness, intense pressure, and low temperatures.
Professor Alan Jamieson from the University of Western Australia emphasizes the significance of temperature in these ecosystems. The Izu-Ogasawara Trench's water is slightly warmer than that of the Mariana Trench, which may play a crucial role in the viability of life at such depths. Researchers suggest that if anyone aims to discover even deeper fish, the Izu-Ogasawara Trench is an ideal location.
Is there a known limit to how deep fish can thrive? According to Prof. Jamieson, this limit is approximately 8,400 meters. Beyond this depth, the biochemical processes that protect deep-sea fish cells from high pressures become ineffective.
Section 2.1: Adaptations to Life in Extreme Depths
What do the fish of these profound depths look like? Contrary to common perceptions of deep-sea creatures being black with large teeth, adaptations to darkness are more nuanced.
“Adaptations to deep-sea life are not as apparent as one might think,” explains Prof. Jamieson. “Fish in this environment, such as those in the denfishes family, successfully thrive without swim bladders, as maintaining a gas-filled chamber would be challenging under such pressure.” Another adaptation involves their skin; rather than scales, many deep-sea fish are covered with a gelatinous layer.
Section 2.2: Capturing the Deepest Fish
In addition to filming the fish at 8,336 meters, the expedition also achieved a notable milestone by capturing several specimens at a slightly shallower depth of 8,022 meters. These fish belong to the Pseudoliparis belyaevi species, marking the first time fish have been confirmed captured at depths below 8 kilometers.
Da Vinci’s Secret Ingredient Found in Your Fridge!
Recent research has shown that past master painters used a certain ingredient when painting their oil paintings…
Thank you for reading! If you enjoyed this article, please show your appreciation with some claps, follow me, or consider leaving a tip. Your support is greatly appreciated!