Exploring the James Webb Space Telescope: A Quantum Leap in Astronomy
Written on
Chapter 1: The Evolution of Space Telescopes
The launch of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) marks a significant advancement in astronomical observation, with capabilities that far surpass those of its predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope.

Astronomers have faced numerous challenges since the dawn of the field. One major issue is that celestial bodies emit electromagnetic radiation, yet the human eye can only perceive a narrow band of the visible spectrum. Additionally, detecting the wavelengths of distant objects poses its own difficulties, further complicated by Earth's atmosphere, which distorts incoming data due to environmental factors such as wind and temperature fluctuations.
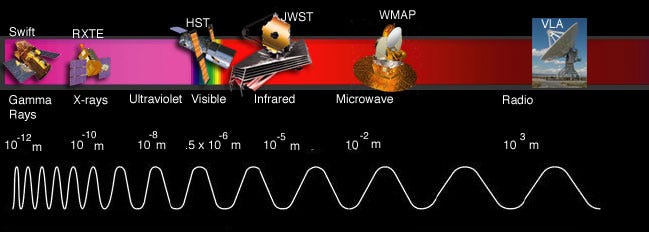
While ground-based telescopes have been effective in addressing some of these challenges, the atmosphere remains a significant barrier. Emissions from distant stars can be altered as they pass through various atmospheric layers, leading to loss of information.
Section 1.1: The Hubble Space Telescope
NASA credits theoretical physicist and astronomer Lyman Spitzer for proposing the concept of a large space telescope back in 1946. Spitzer argued that a space-based observatory would yield clearer images across a broader spectrum than ground-based telescopes.
Ground-based telescopes have limitations, but space-based options, like the Hubble Space Telescope, have provided solutions to many of these problems. Hubble, launched in 1990, orbits at an altitude of approximately 350 miles, away from the Earth's atmospheric distortions, capturing images with ten times the clarity of ground-based instruments.
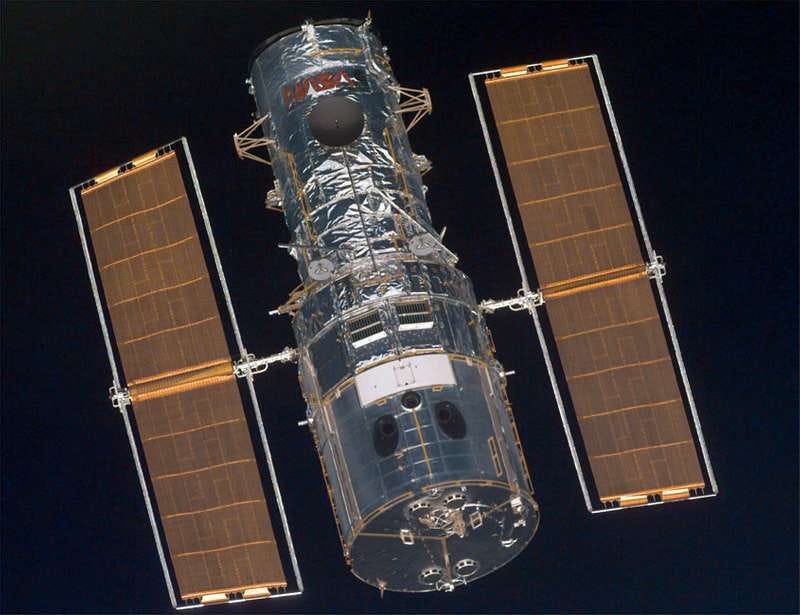

Hubble's dimensions are comparable to those of a large school bus, measuring 43.5 feet (13.3 meters) in length and 14 feet (4.3 meters) in diameter at its widest point. On Earth, it weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,340 kilograms), but in the microgravity of space, it appears weightless.
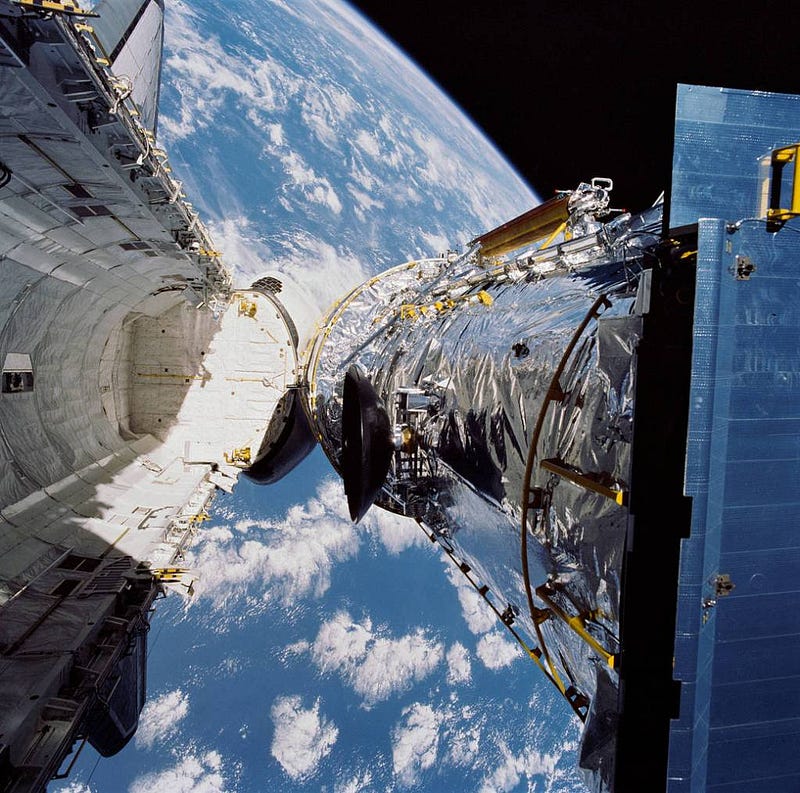

Despite its groundbreaking capabilities, Hubble is not powerful enough to unveil many of the universe's secrets, necessitating the need for a more advanced telescope.
Chapter 2: The James Webb Space Telescope
NASA's JWST represents a new frontier in astronomical research. Initially scheduled for an earlier launch, delays and escalating costs pushed the JWST's budget to over $8 billion, underscoring the complexities involved in creating such an intricate space instrument.
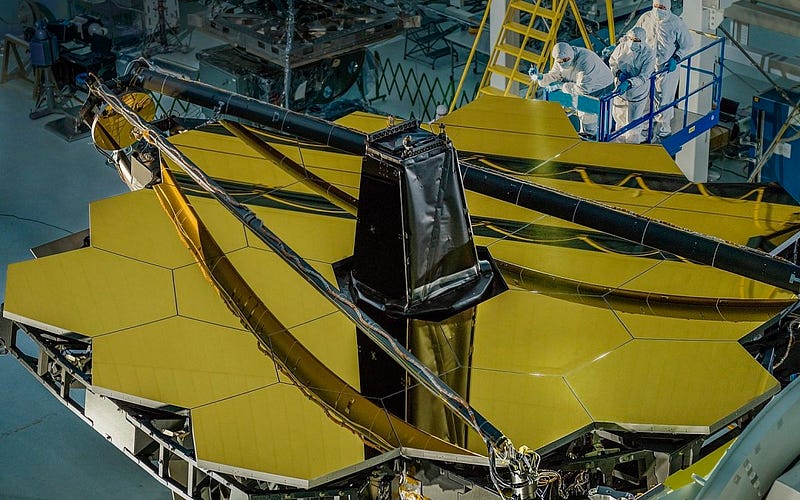
The JWST's design is a departure from that of Hubble, featuring a much larger primary mirror measuring 21 feet (6.4 meters) in diameter, constructed from 18 gold-plated beryllium hexagonal segments.
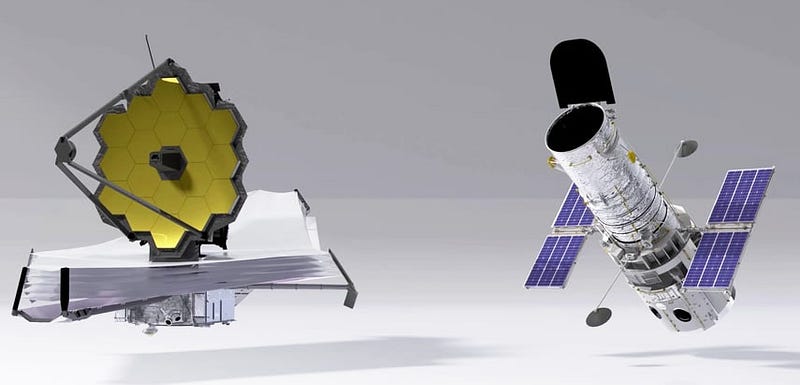
This innovative design allows for greater light collection and a larger field of view, surpassing Hubble's capabilities significantly. In fact, JWST's collecting area is about 6.25 times larger than Hubble's, making it a powerful tool for observing infrared light.
The video titled "Did the James Webb Space Telescope Change Astrophysics?" provides insights into how this telescope is reshaping our understanding of the cosmos.
Section 2.1: The Segmented Mirror Approach
The segmented mirror design is not entirely new; it has roots in earlier projects like the Keck Observatory, which began operation in 1993. Each of JWST's 18 mirror segments is designated as A, B, or C, reflecting a meticulous design that optimizes light capture.
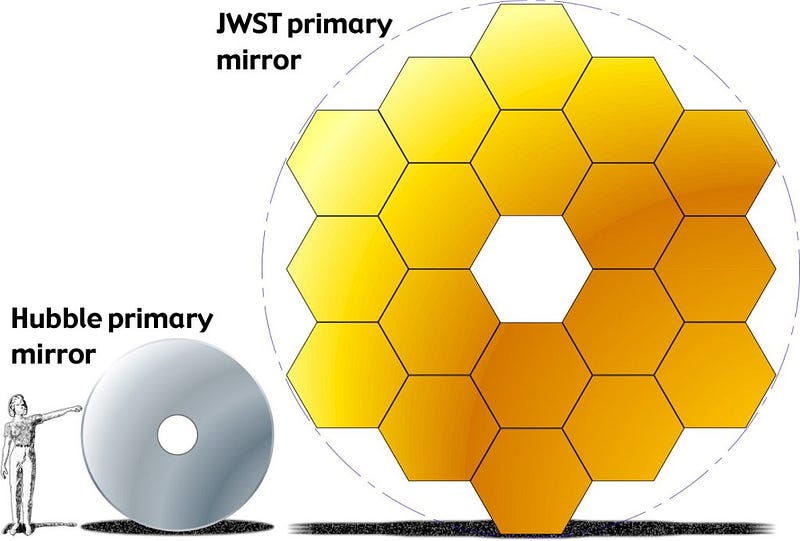
By positioning JWST in space, the gravitational forces acting on it are significantly reduced, allowing for a lighter structure compared to Earth-based telescopes. Each of the segments weighs about 46 pounds (20 kilograms).
Section 2.2: Orbiting the Lagrange Point
JWST will orbit the sun at Lagrange Point 2 (L2), approximately 1.5 million kilometers (1 million miles) from Earth. This unique position allows the telescope to maintain a temperature of minus 388 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 233 degrees Celsius), which is critical for infrared observations.
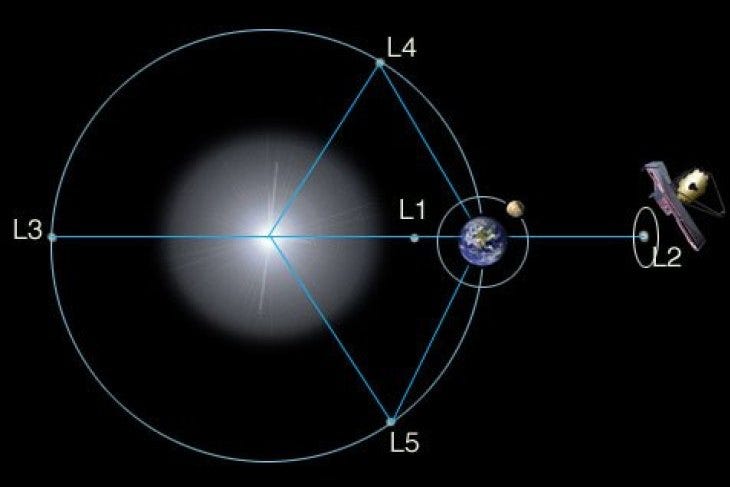
Jonathan P. Gardner, the Deputy Senior Project Scientist for JWST, emphasizes that the cold environment of deep space is vital for observing infrared light, as the telescope must remain cooler than the heat it aims to detect.
In the video "New Telescope Can See WAY MORE than JWST and Hubble," explore the advancements in telescope technology and how they expand our understanding of the universe.
The James Webb Space Telescope is poised to revolutionize our view of the universe, enabling unprecedented observations that will deepen our understanding of cosmic phenomena.