Upgrade Your Internet Experience with Wi-Fi 6 Today!
Written on
Understanding Wi-Fi and Its Evolution
Are you tired of your streaming services buffering or experiencing dropped calls during virtual meetings? The issue may not lie with your Internet Service Provider (ISP), but rather with your current Wi-Fi setup. Enter Wi-Fi 6— a solution designed to address these concerns.

Imagine watching your favorite show, and just as the plot thickens, your screen freezes. Frustrated, you wonder if your internet connection is truly reliable. With the average household now possessing around 25 devices, as reported by Reuters in June 2021, it's no wonder that traditional Wi-Fi struggles to keep up.
The Challenges of Legacy Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi operates as a shared medium, meaning that as more devices connect, the available bandwidth diminishes. As the number of connected devices increases, the network's performance can suffer significantly. Wi-Fi 6 aims to change that paradigm.
This guide will discuss the following aspects of Wi-Fi 6:
- The fundamentals of Wi-Fi technology.
- The limitations of previous Wi-Fi standards.
- Improvements brought by Wi-Fi 6.
- How you can leverage these advancements, including a review of various routers and access points.
Key Features of Wi-Fi
At its core, Wi-Fi provides wireless connectivity within a limited range, typically confined to a building, while delivering high-speed internet. The effectiveness of Wi-Fi is influenced by the radio frequency bands it utilizes, which include 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the newly introduced 6 GHz.
Unfortunately, these bands are unregulated, leaving them susceptible to interference from other networks. This can hinder performance, as multiple networks may disrupt each other.
To better understand the various Wi-Fi standards, here's a simplified overview:
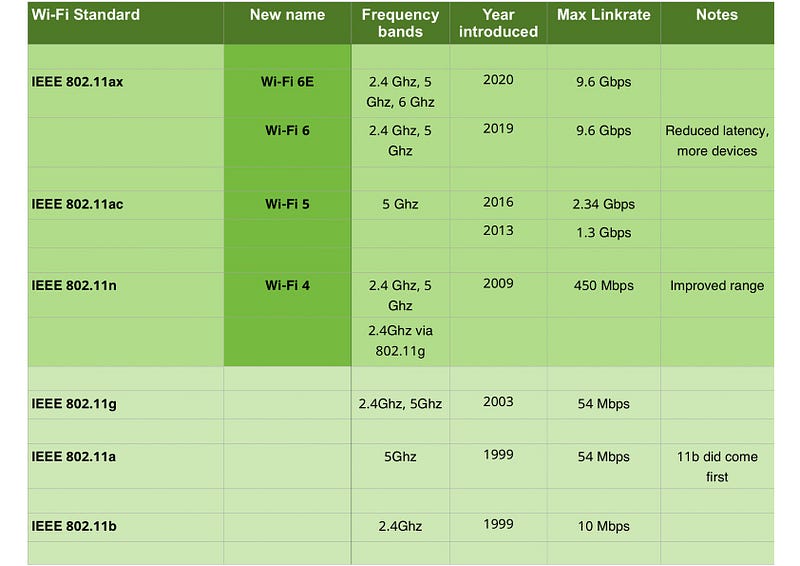
The Advantages of Wi-Fi
The true strength of Wi-Fi lies in its ability to provide internet access throughout your home. Users today take for granted the convenience of connecting multiple devices without the hassle of wired connections. However, businesses often still rely on wired networks for greater reliability and speed.
The Downsides of Wi-Fi and the Solutions Offered by Wi-Fi 6
In its earlier iterations, Wi-Fi often required users to sacrifice performance for convenience. This posed challenges for demanding applications like video streaming and voice calls. Additionally, security was a concern, with early encryption protocols being inadequate.
Wi-Fi 6 addresses these issues head-on. As noted earlier, multiple devices share the same bandwidth, which can lead to competition for resources when streaming or making calls.
Traditionally, when one device transmitted data, it monopolized the channel, preventing others from transmitting simultaneously. Wi-Fi 6 improves this by introducing sub-channels, allowing devices to communicate without waiting for others to finish.
This technology, known as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), optimizes bandwidth use and enhances overall performance.
Another issue is access competition; devices often wait unnecessarily, even if traffic originates from distant networks. Wi-Fi 6 mitigates this by assigning colors to access points, enabling devices to disregard irrelevant traffic.
Combining OFDMA and Overlapping Basic Service Sets (OBSS) brings Wi-Fi closer in performance to wired Ethernet connections, enabling businesses to rely more on wireless networks.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 employs Beamforming technology, which directs data specifically to the intended device rather than broadcasting it to all devices on the network.
Security has also seen significant improvements. The original WEP encryption was weak, leading to the development of WPA and subsequently WPA2. Wi-Fi 6 now features WPA3, which offers enhanced protection against modern threats.
Leveraging Wi-Fi 6 for Your Home Network
To fully utilize the benefits of Wi-Fi 6, consider the following options:
- Replace your existing router with a Wi-Fi 6 model.
- Enhance your current setup by adding a Wi-Fi 6 access point or a mesh network device.
When selecting a router, ensure it is compatible with your ISP’s configuration. My personal experience upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 access point was seamless, taking only about 15 minutes to set up.
Will my existing devices work with Wi-Fi 6?
Yes, Wi-Fi 6 is designed to be backward compatible, so older devices should work without issues. However, they may not benefit from the full capabilities of Wi-Fi 6.
Is it time for an upgrade?
After upgrading my outdated NETGEAR Orbi system to a TP-Link mesh network, I noticed a remarkable improvement in both speed and coverage, eliminating dead zones in my home.
What about you? Are you considering a transition to a Wi-Fi 6 network? If you’ve already made the switch, what has been your experience?
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 6 presents a significant leap forward in wireless technology, promising improved performance, enhanced security, and better overall connectivity for households and businesses alike.
Helpful Resources:
This video provides insights on troubleshooting common issues related to YouTube not working over Wi-Fi, helping you optimize your streaming experience.
Learn about the reasons behind frequent disconnections when using screen mirroring and how to resolve them for a smoother experience.
Bibliography
- What is Wi-Fi 6?; Intel.
- Wi-Fi Security: WEP vs WPA or WPA2; Avast.
- Wi-Fi 6: The compatibility issues you should know about; Eye Networks.
- What is Wi-Fi 6E?; Juniper Networks.
- How WiFi Works; Howstuffworks.
- Wi-Fi 6E is here; Broadcom.
Appendix A: Router and Access Point Reviews
Router Reviews:
- Asus RT-AX86: 4.5 stars; excellent throughput.
- Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500: 4.5 stars; supports 6 GHz band.
- TP-Link Archer GX90: 5 stars; ideal for gaming.
Access Point Reviews:
- Netgear WAX214: Affordable and easy to configure.
- TP-Link EAP660HD: Cost-effective with cloud support.
- Asus ZenWiFi AX (XT8): Exceptional performance and security features.